IDH was incorporated in July 2011 and established to provide specialist Scaffold Design, Formwork Design & general Temporary Works Design consultancy serving Sub-Contractors, Main Contractors and Client developers.
How Do Ties Work ?
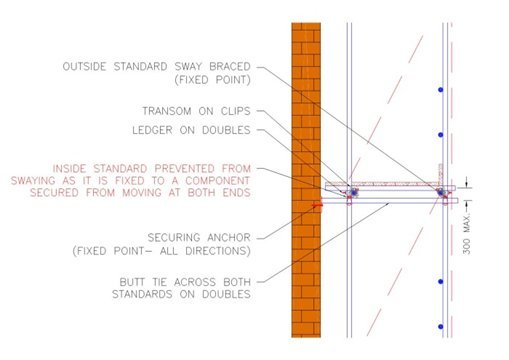
To stabilise a scaffold we tie it to the adjacent building as the scaffold is erected. Conventionally this is done by means of an anchor fixing in to the façade and then a tie tube on doubles across both standards and all within 300mm of the ledger / standard interface. This point being a node (point of NO DE-flection).
Depending on a number of factors such as geographic location, netting, sheeting, height and load we determine in the design process what tie pattern to adopt and the frequency of ties.
Ties however, undertake more than one function.
Firstly they prevent the scaffold from pulling away from the building – but if this is the case why not fix them at all standards, or for that matter at every 4 standards for instance.
In addition to providing this pull restraint, they also stabilise the scaffold from swaying parallel to the building and contribute to the effective length of the standard in question.
Sway stability parallel to the building is provided by a combination of the tie tube and the face brace. By installing the correct sway bracing, the outside line is prevented from moving parallel to the building. By securing the tie tube to the building façade and the outside line we now have a tube which is prevented from movement at both ends. When the inside line is now secured to this tube (with doubles) the inside line is now also prevented from moving parallel to the building by the bending resistance of this tie tube. This is why inside lines are not sway braced!
In some designed circumstances it may be a requirement to tie to the inside line only or miss ties altogether. When these scenarios occur the scaffold should be designed as we no longer have that sway restraint present and alternative measures need to be considered such as plan bracing or V-ties.
For more explanation on this and other technical scaffold design subjects visit the IDH blog: http://www.idh-design.co.uk/blog/
Author: Tim Burt on Google+