Rilmac Scaffolding Appoints New Southern Director
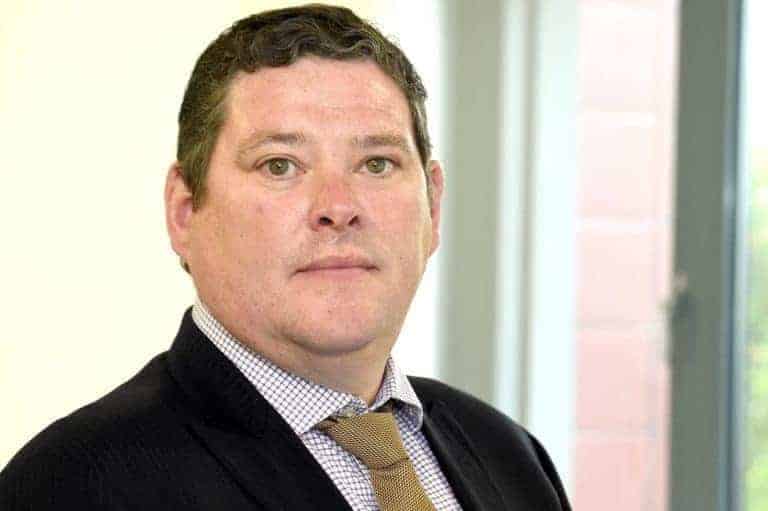
Rilmac Scaffolding Ltd has announced the appointment of Paul Wallis in the role of Director – Southern. Wallis will be based at the Rilmac Depot in Northampton and have responsibility for the whole southern region, including London and the Home Counties.
The Northampton Depot has seen impressive growth since opening just over three years ago and Wallis will be looking to grow on the success, overseeing such prestigious projects as the scaffolding for a new student accommodation village at Warwick University.
Rilmac says Paul has over 30 years’ experience in the scaffolding industry, most recently as General Manager for Hallam Scaffold Ltd. His vast experience and depth of knowledge will be a great addition to the team.
In his free time, Paul is a bit of a petrolhead, driving fast cars and attending many motorsport events. He is hoping to get away from the grid quickly as he settles into his new role!
Denholm Industrial Acquires Access Systems Provider ALPS
Denholm Industrial has announced the acquisition of Access Lifting Pulling & Safety Ltd, commonly known as ALPS, which was completed on 14th September 2018 for an undisclosed sum.
The acquisition expands Denholm Industrial’s existing engineered capabilities on structures that are difficult to access and the combined capabilities establish a fully comprehensive scaffolding and access solutions provider.
Based near Sheffield, ALPS designs and implements bespoke engineered access solutions and specialises in suspended access and lifting applications. The company has developed its skills, expertise and methodologies to safely deploy suspended access equipment, modular mobile platforms and specialist industrial rope access technicians, overcoming the challenges of accessing large or complex structures that are difficult or impractical to access using conventional scaffolding methods.
The acquisition of ALPS enhances the existing engineered scaffolding and access capabilities of Denholm Industrial and its subsidiaries and the combined businesses provide a fully comprehensive single-supplier service that offers flexible and efficient access solutions.
 Denholm Industrial Group Managing Director Steve Hill said: “ALPS has a track record of accessing some of the UK’s most iconic and difficult to reach landmarks and structures and combining our skills and competences creates an attractive proposition for customers of ALPS, Denholm Industrial Services and SES, our Midlands-based scaffolding business. Together, we offer a comprehensive set of capabilities to meet both routine and bespoke access requirements, which reduces the number of on-site interfaces for our customers when they are managing major construction, maintenance and repair projects.”
David Simm of ALPS said: “Combining the skills, experience and expertise of ALPS and Denholm Industrial was compelling for me. We have developed and honed our specialist access skills over the past 20 years, particularly as structures have become bigger and more challenging to access. Similarly, Denholm Industrial has built up a family of recognised and well-respected scaffolding and access brands and as part of a larger family-run group, shares our work ethic and total commitment to health and safety. The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial establishes a truly complete engineered access solutions provider.”
The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial follows previous acquisitions of Elite Scaffolding in April 2018 and Scaffold Erection Services (SES) in May 2016, two well-regarded access and scaffolding companies in the south west of England and the Midlands respectively.
Denholm Industrial Group Managing Director Steve Hill said: “ALPS has a track record of accessing some of the UK’s most iconic and difficult to reach landmarks and structures and combining our skills and competences creates an attractive proposition for customers of ALPS, Denholm Industrial Services and SES, our Midlands-based scaffolding business. Together, we offer a comprehensive set of capabilities to meet both routine and bespoke access requirements, which reduces the number of on-site interfaces for our customers when they are managing major construction, maintenance and repair projects.”
David Simm of ALPS said: “Combining the skills, experience and expertise of ALPS and Denholm Industrial was compelling for me. We have developed and honed our specialist access skills over the past 20 years, particularly as structures have become bigger and more challenging to access. Similarly, Denholm Industrial has built up a family of recognised and well-respected scaffolding and access brands and as part of a larger family-run group, shares our work ethic and total commitment to health and safety. The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial establishes a truly complete engineered access solutions provider.”
The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial follows previous acquisitions of Elite Scaffolding in April 2018 and Scaffold Erection Services (SES) in May 2016, two well-regarded access and scaffolding companies in the south west of England and the Midlands respectively.
 Denholm Industrial Group Managing Director Steve Hill said: “ALPS has a track record of accessing some of the UK’s most iconic and difficult to reach landmarks and structures and combining our skills and competences creates an attractive proposition for customers of ALPS, Denholm Industrial Services and SES, our Midlands-based scaffolding business. Together, we offer a comprehensive set of capabilities to meet both routine and bespoke access requirements, which reduces the number of on-site interfaces for our customers when they are managing major construction, maintenance and repair projects.”
David Simm of ALPS said: “Combining the skills, experience and expertise of ALPS and Denholm Industrial was compelling for me. We have developed and honed our specialist access skills over the past 20 years, particularly as structures have become bigger and more challenging to access. Similarly, Denholm Industrial has built up a family of recognised and well-respected scaffolding and access brands and as part of a larger family-run group, shares our work ethic and total commitment to health and safety. The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial establishes a truly complete engineered access solutions provider.”
The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial follows previous acquisitions of Elite Scaffolding in April 2018 and Scaffold Erection Services (SES) in May 2016, two well-regarded access and scaffolding companies in the south west of England and the Midlands respectively.
Denholm Industrial Group Managing Director Steve Hill said: “ALPS has a track record of accessing some of the UK’s most iconic and difficult to reach landmarks and structures and combining our skills and competences creates an attractive proposition for customers of ALPS, Denholm Industrial Services and SES, our Midlands-based scaffolding business. Together, we offer a comprehensive set of capabilities to meet both routine and bespoke access requirements, which reduces the number of on-site interfaces for our customers when they are managing major construction, maintenance and repair projects.”
David Simm of ALPS said: “Combining the skills, experience and expertise of ALPS and Denholm Industrial was compelling for me. We have developed and honed our specialist access skills over the past 20 years, particularly as structures have become bigger and more challenging to access. Similarly, Denholm Industrial has built up a family of recognised and well-respected scaffolding and access brands and as part of a larger family-run group, shares our work ethic and total commitment to health and safety. The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial establishes a truly complete engineered access solutions provider.”
The acquisition of ALPS by Denholm Industrial follows previous acquisitions of Elite Scaffolding in April 2018 and Scaffold Erection Services (SES) in May 2016, two well-regarded access and scaffolding companies in the south west of England and the Midlands respectively. Four Workers Dead After Scaffolding Collapses At Multi Storey Building
A large section of scaffolding has collapsed after a tractor-trailer, used for loading and unloading materials, accidentally backed into the scaffolding according to sources.
Four construction workers were killed and five injured on Sunday after the accident that happened at a multistorey building under-construction in Noida, India.
Police have said the accident seemed to have occurred because a tractor-trailer backed into the structure. The entire section collapsed bringing the workers down with it and falling onto the tractor killing the driver. The injured workers were rushed to various hospitals but three other workers succumbed to their injuries and were pronounced dead.
Police are investigating the accident and safety lapses on the site. A police spokesperson said: “There definitely would have been some safety lapses. If the structure was sturdy enough, it wouldn’t have collapsed in this manner.”
A stonemason who had been working on the site alleged that the accident was due to negligence he said: “The ties that hold the scaffolding to the building were removed during the process of attaching glass. This caused the scaffolding to become unstable.”
Layher Scaffolding and Event Systems Take Centre Stage
The use of Layher scaffolding, access and event equipment for a specialist project in York undertaken by Acorn Events Structures is, in every sense, dramatic.
Award-winners Acorn have designed and installed a faithful recreation of Shakespeare’s celebrated Rose Theatre for Lunchbox Productions who are running a series of theatrical events throughout the summer and autumn at the site. “The project is a genuine ‘one-off’ and huge credit is due to Acorn Managing Director, Andy Nutter and his team,” says Sean Pike, Layher’s UK Managing Director. “Their use of a wide range of our scaffolding and event products pays testimony to both their ability and creativity and the versatility of our equipment, and we are delighted to have played a key role in the work.” The remarkable structure reflects both the design and functional elements of the original ‘London Rose Playhouse’ that dates from 1587. The 13-sided design can accommodate a full width two-level stage together with an audience numbering 600 on three covered tiers, with a further 350 ‘groundlings’ underneath an open roof. “The theatre utilises 1500 square metres of corrugated iron panels and timber elements, but the main supporting structure itself has been created using Layher’s equipment including the company’s Allround scaffolding and event seating systems,” says Andy Nutter at Acorn Events. “The roof over the seating blocks, both upper and lower stage platforms, on-stage staircases and a beamed roof across the stage also feature Layher equipment with its ease of handling, choice of fixing positions and integration all key considerations.”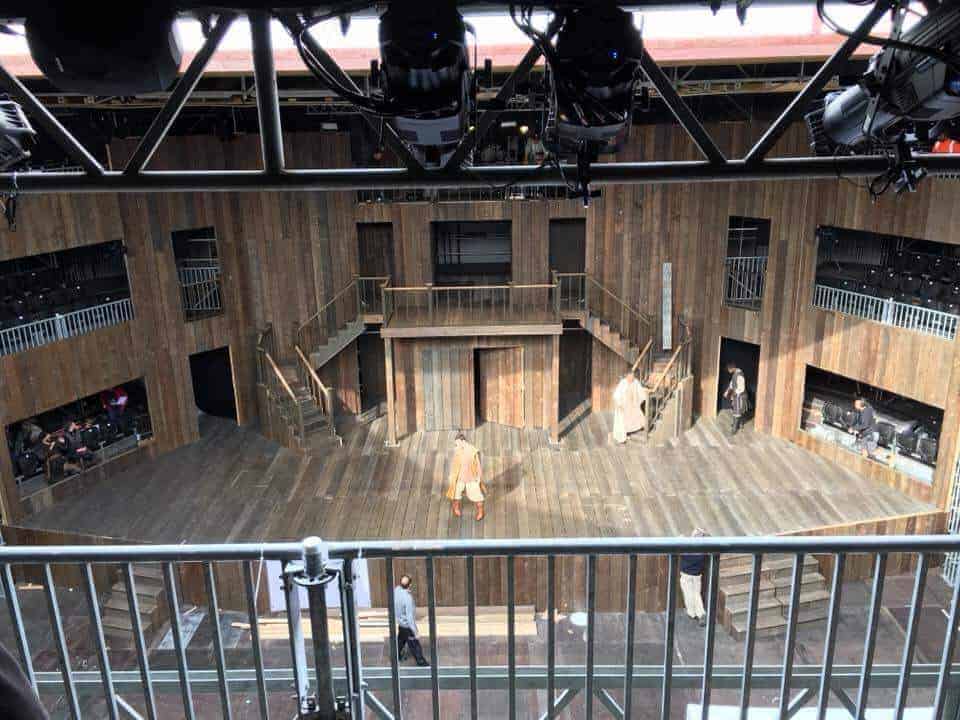 Built in less than three weeks on a car park in the centre of York, the Rose Theatre Project is part of a regional commitment to bringing exciting theatrical experiences to the north of England. Its thoroughly bespoke nature and the requirement to follow a very rigid, historical layout and dimensions are reflected in both Acorn Event’s capabilities and the suitability of Layher equipment to meet the requirements of projects of all shapes and sizes.
“We are delighted to be part of such an important local project which creates a cultural legacy for our community while supporting local industry,” adds Andy Nutter. “We’ve worked closely with our client to design and engineer a unique and functional performance area which positions audience members within just 15 metres of the action, with the aim of presenting Shakespeare’s plays in a similar environment to that which would have been enjoyed 400 years ago.”
“It is a highly impressive blend of historical objectives and modern methods of construction, and everybody concerned should take a bow for their performance,” concludes Sean Pike.
Built in less than three weeks on a car park in the centre of York, the Rose Theatre Project is part of a regional commitment to bringing exciting theatrical experiences to the north of England. Its thoroughly bespoke nature and the requirement to follow a very rigid, historical layout and dimensions are reflected in both Acorn Event’s capabilities and the suitability of Layher equipment to meet the requirements of projects of all shapes and sizes.
“We are delighted to be part of such an important local project which creates a cultural legacy for our community while supporting local industry,” adds Andy Nutter. “We’ve worked closely with our client to design and engineer a unique and functional performance area which positions audience members within just 15 metres of the action, with the aim of presenting Shakespeare’s plays in a similar environment to that which would have been enjoyed 400 years ago.”
“It is a highly impressive blend of historical objectives and modern methods of construction, and everybody concerned should take a bow for their performance,” concludes Sean Pike. SMART Inspector App records over 100,000 inspections for Lyndon Scaffolding
Lyndon Scaffolding Plc has now carried out more than 100,000 scaffold inspections using SMART Scaffolder’s SMART Inspector app.
Sources say the UK’s largest independent scaffolding firm – Lyndon Scaffolding Plc has been using SMART Inspector app since February 2017. Their scaffold inspectors have now carried out more than 100,000 weekly scaffold inspections on sites across the country, from remote Scottish glens, like Orchy Viaduct in Oban, to the heart of the capital, on iconic jobs like Coal Drops Yard at King’s Cross, and everywhere in between. Developed in partnership with Lyndon, the breakthrough SMART Inspector app from CADS improves and streamlines the firms 100’s of weekly scaffold inspections – legally required by the 2005 Work at Height Regulations. Lyndon Scaffolding CEO, Rob Lynch said: “We are more than happy with the inspection app, which has not only improved the quality of our reports but also transformed the efficiency, leading to better and safer scaffolds Ian Chambers, Sales & Marketing Director at SMART Scaffolder, added: “To have expert clients of the ilk and scale of Lyndon as development partners of our SMART Inspector app has been invaluable to its development and commercial success! We have also had keen interest from many main contractors, house builders and the Health & Safety fraternity. “Across the UK, we have already seen more than 200,000 scaffold inspections signed off on our SMART Inspector app! More and more customers are coming online and recognising the many benefits to their scaffolding businesses, regardless of size. Utilising mobile and cloud technology to help scaffolding firms streamline, speed up, improve safety and go paperless is not just in the future, it’s now.” said Chambers. SMART Inspector is a commercial app available for all scaffolders to download and try out! It’s specifically designed to make the entire inspection process better, faster, and simpler. Providing higher quality inspections, more reliable record keeping and an auditable proof of compliance frees up time for Supervisors and Contract Managers to get on with their work whilst investing in improved site safety. An enhanced and updated Version 4.0 of SMART Inspector is available for free trials now via: https://smartscaffolder.comAIS Training delivers scaffolding training in Ecuador
A leading industrial trainer, AIS Training is helping maritime construction specialist, Jan de Nul, upskill its workers in Ecuador, South America.
An experienced AIS Training instructor visited Ecuador to develop and implement basic scaffolding awareness training with Jan de Nul staff working onboard vessels currently helping in the construction of a new container port in the region. The bespoke course was specially designed by AIS Training to give key Jan de Nul crew members an understanding of health and safety when working around scaffolding which is used on vessels to enable maintenance work. It is the latest in a series of courses developed and delivered by AIS Training for Jan de Nul to embed high health and safety standards across its business. AIS Training instructor, Gary Burke, said: “We were delighted to work with Jan de Nul to improve the skills of its workers in Ecuador. The correct training can have a huge impact on the efficiency and productivity of personnel and this particular course has provided Jan de Nul personnel with an important understanding of the basic health and safety issues surrounding scaffolding onboard vessels. “The UK and AIS Training is renowned across the globe for having the very highest industry standards. As well as being able to deliver world-class training tailored to the client’s requirements, AIS Training is extremely nimble and can mobilise anywhere in the world whenever needed.”Andrew Smith Assumes New Position At Avontus
As Avontus Software continues to grow, Andrew Smith has assumed the new role of Vice President of Operations. This change will ensure that Avontus continues to deliver the finest pre- and post-sales support. In his new role Andrew will be responsible for the operational and customer-facing areas of the business globally. “Ensuring our customers have the best user experience from sale to support is critical, and as we expand our software offering and market presence it is essential that we remain customer-focused,” said Smith.
Prior to joining Avontus in 2014, Andrew spent 11 years in the scaffold industry working with both large and small scaffolding contractors. Andrew has extensive experience in project, site, contract, and branch management, and he is an active member of scaffolding associations in both North America and Europe.
“First and foremost, Avontus is focused on the customer. As we expand and enhance our product offerings, having Andrew in place will ensure we continue to meet our customers’ expectations,” commented Brian Webb, CEO/Founder. “Andrew is well-known and well-liked in the industry and we are fortunate to have him as part of our team,” Brian added.
With the new releases of Scaffold Viewer and Scaffold Designer expected in the coming weeks, augmented reality is being added to the already successful suite of scaffold design and visualization tools, which saw the addition of virtual reality in 2017.
“Being a technology partner for our customers will continue to be a core value as we expand our sales and support teams,” added Smith, “and ensuring that we have a scalable infrastructure in place will be critical to our customer success moving forward.”
GKR launches support initiative for Mental Health & Wellbeing
GKR Scaffolding has today announced an enhanced support and awareness programme for mental health, accessible to its entire staff via its Betterfuture – Better Mental Health initiative.
It has been widely reported that the construction industry has a problem with mental health. In response, GKR has spent the last year raising awareness of mental health amongst staff.
To mark World Mental Health Day, the company owners and the Senior Leadership Team have all signed the Building Mental Health Charter as a sign of commitment to the workforce in every division.
The business commits to reducing the stigma around mental health, and to provide assistance and signpost people to the support they need.
Opening up the conversation about mental health has already had a profound impact. It has encouraged some of those needing support to step forward, highlighting the importance of not only raising awareness but also having a support infrastructure in place.
The Betterfuture: Better Mental Health programme has been built using the framework introduced by Building Mental Health; an industry-wide initiative joining construction businesses with active and freely available support, information and advice.
GKR is about to train its second round of Mental Health First Aiders, on its way to ensuring the business has as many MHFA’s as physical first aiders. With a growing number of MHFAs in place, GKR are taking the programme beyond building awareness.
Using the Lighthouse Construction Industry Charity Helpline, anyone needing assistance is signposted to appropriate support. Additionally, it has been recognised that lifestyle and general wellbeing plays a huge part in influencing mental health. GKR is actively promoting information on these influencers to help individuals support their own mental health.
Information and advice on triggers such as sleep, nutrition, fitness, drug and alcohol use, financial health and work/life balance is being rolled out to staff, working towards a Wellbeing Week that will be hosted in early 2019.
Health & Safety Director, Peter Cullen said: “As an industry, we’ve focused very much on safety in the last decade, and less so on health. By acknowledging the fact we have a mental health issue and putting support frameworks in place, it gives us an opportunity to discuss other aspects of our people’s wellbeing.
On top of the obvious things like diet and fitness, huge consideration needs to be given to some of the areas that genuinely cause our staff concern, such as work-related stress, fatigue and worries over personal finances. Our programme takes mental health beyond just raising awareness and offers a full circle of support to address everyone’s overall wellbeing.”
SMART Scaffolder Launches Upgraded Inspection and Handover Apps
Developed by CADS, version 4.0 of the ground-breaking scaffolding apps is a major upgrade, the makers say. The new version now has enhanced functionality that allows users to record diary notes, photos, audio and video against a scaffold during the weekly inspection or as part of the handover to a client.
The apps also now allow users to download a transcript from the recorded audio or the video. This enables you to record inspection or handover notes audibly into your smart phone or tablet simply using the app (say on a wet, rain-soaked site) and these notes will be transcribed into a document.
 Notes can then be sent back to the desktop management console by the app and logged against the scaffold being inspected or handed over, where they can be filtered by category, e.g. blocked access, theft of boards etc. Users can read the transcript or listen/watch the full recording and make edits accordingly.
The added functionality to the scaffolding apps allows for even better, more accurate inspections and handovers of scaffolding and access jobs. The apps are now even more efficient, modern and environmentally responsible. The paperless set-up is backed up by cloud-based technology for accurate and auditable storage of reports with no need for rekeying.
The new SMART Inspector and Handover app functionality allows users to:
Notes can then be sent back to the desktop management console by the app and logged against the scaffold being inspected or handed over, where they can be filtered by category, e.g. blocked access, theft of boards etc. Users can read the transcript or listen/watch the full recording and make edits accordingly.
The added functionality to the scaffolding apps allows for even better, more accurate inspections and handovers of scaffolding and access jobs. The apps are now even more efficient, modern and environmentally responsible. The paperless set-up is backed up by cloud-based technology for accurate and auditable storage of reports with no need for rekeying.
The new SMART Inspector and Handover app functionality allows users to:
 Ian Chambers, Sales & Marketing Director at SMART Scaffolder said: “We are constantly evolving our market-leading scaffolding software solutions and this Version 4.0 is a major step change in two of our most popular products. As ever, the software update is aimed at making life easier and more efficient in all of its many uses for all of our many users.
“We are sure the apps will be welcomed by existing converts to the many benefits of the SMART Scaffolder product range as well as newcomers.”
Ian Chambers, Sales & Marketing Director at SMART Scaffolder said: “We are constantly evolving our market-leading scaffolding software solutions and this Version 4.0 is a major step change in two of our most popular products. As ever, the software update is aimed at making life easier and more efficient in all of its many uses for all of our many users.
“We are sure the apps will be welcomed by existing converts to the many benefits of the SMART Scaffolder product range as well as newcomers.”
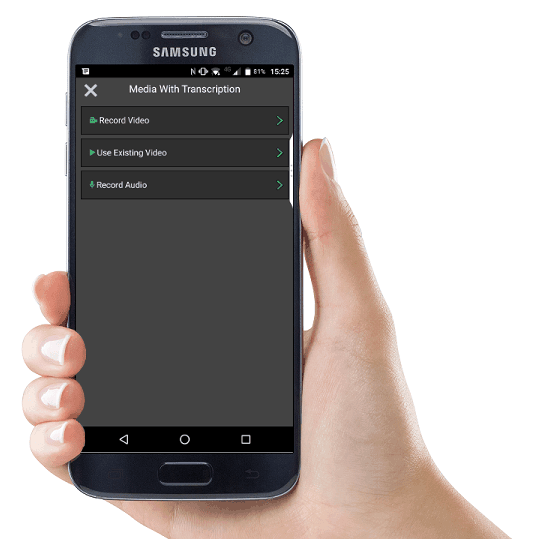 Notes can then be sent back to the desktop management console by the app and logged against the scaffold being inspected or handed over, where they can be filtered by category, e.g. blocked access, theft of boards etc. Users can read the transcript or listen/watch the full recording and make edits accordingly.
The added functionality to the scaffolding apps allows for even better, more accurate inspections and handovers of scaffolding and access jobs. The apps are now even more efficient, modern and environmentally responsible. The paperless set-up is backed up by cloud-based technology for accurate and auditable storage of reports with no need for rekeying.
The new SMART Inspector and Handover app functionality allows users to:
Notes can then be sent back to the desktop management console by the app and logged against the scaffold being inspected or handed over, where they can be filtered by category, e.g. blocked access, theft of boards etc. Users can read the transcript or listen/watch the full recording and make edits accordingly.
The added functionality to the scaffolding apps allows for even better, more accurate inspections and handovers of scaffolding and access jobs. The apps are now even more efficient, modern and environmentally responsible. The paperless set-up is backed up by cloud-based technology for accurate and auditable storage of reports with no need for rekeying.
The new SMART Inspector and Handover app functionality allows users to:
- Record the progress of the scaffold build or dismantle
- Record any problems, such as lack of access or conflict with other works
- Record any variation requests
- Record to show that the site is clear when you have completed the job
- All of this is sent back from the app to the management console, so those in the office can track the progress of the work and be aware of issues.
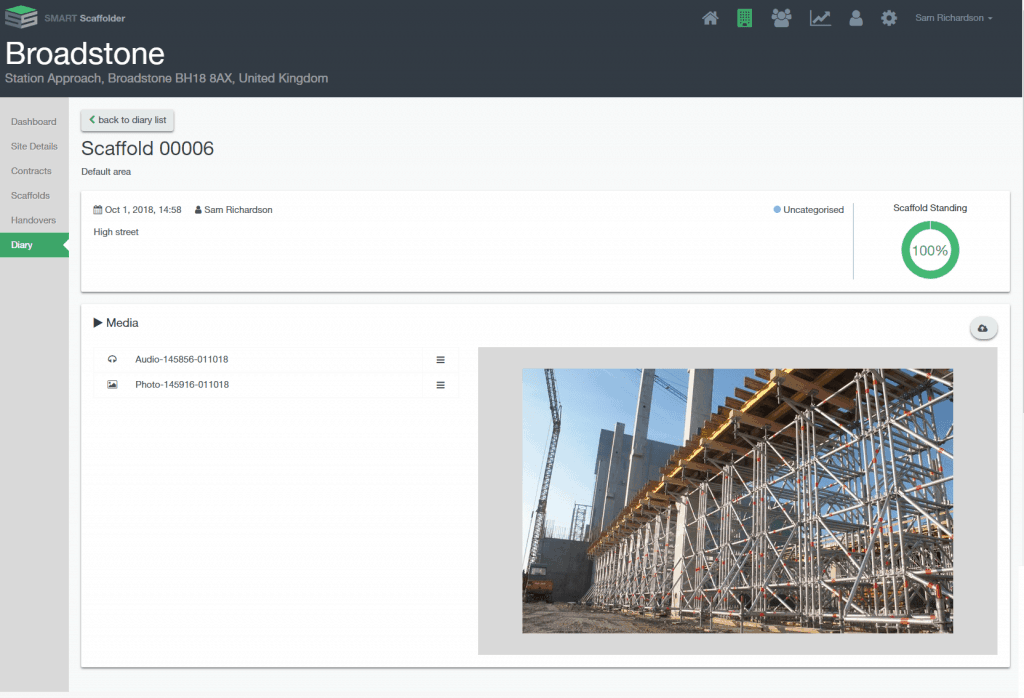 Ian Chambers, Sales & Marketing Director at SMART Scaffolder said: “We are constantly evolving our market-leading scaffolding software solutions and this Version 4.0 is a major step change in two of our most popular products. As ever, the software update is aimed at making life easier and more efficient in all of its many uses for all of our many users.
“We are sure the apps will be welcomed by existing converts to the many benefits of the SMART Scaffolder product range as well as newcomers.”
Ian Chambers, Sales & Marketing Director at SMART Scaffolder said: “We are constantly evolving our market-leading scaffolding software solutions and this Version 4.0 is a major step change in two of our most popular products. As ever, the software update is aimed at making life easier and more efficient in all of its many uses for all of our many users.
“We are sure the apps will be welcomed by existing converts to the many benefits of the SMART Scaffolder product range as well as newcomers.” 









